What is Google Ads?
In short, Google Ads is a paid advertising platform where advertisers bid to display brief advertisements, service offerings, product listings, or videos to web users.
Formerly known as Google Adwords, in 2018 Google rebranded the advertising platform to Google Ads.
Google Ads allows businesses to create, tailor and monitor ads targeting users at the exact moment they are interested in products or services provided by your company. Using Google Ads can be a great way to help increase profitability in your business. As a disclaimer, this article focuses mainly on the PPC search ads but does include information on other types of ads.
How Does Google Ads Work?
Google Ads comprises several moving parts which for this article, we’ll categorise into 5 main topics; Cost, Quality Score, Bidding, Ads & Other.
Cost
One of the most commonly asked questions about Google Ads is “How much does it cost?”. This is not an easy question to answer, because the answer is ambiguous. Essentially, the answer is as much or as little as you like.
Google Ads works on a model that means you pay on a per-click, per-view, per-engagement or per-mille basis, meaning that your budget can be anything you want.
CPC (cost per click) is the most frequent method of bidding, commonly used with search and display ads – we’ll cover the difference in ads later on in the article. This method means you set a bid for a keyword, in which you then compete with other advertisers for the users’ click.
There are other bidding methods available, such as CPV (cost per view), CPE (cost per engagement) and CPM (cost per mille - per 1000 ad impressions). Some of these bidding methods apply directly to display and/or video ads only.
You can set daily budgets per campaign, shared budgets for all campaigns to operate from, or you can set monthly budgets to the account, meaning you’ll never spend more than you’ve allocated.
Quality Score
You may have heard of “quality score” before, in relation to Google Ads. This score is measured on a scale from 1–10, is available at the keyword level and is determined by the following factors:
- Expected click-through rate (CTR): The likelihood that your ad will be clicked when shown.
- Ad relevance: How closely your ad matches the intent behind a user's search.
- Landing page experience: How relevant and useful your landing page is to people who click your ad.
Essentially, the higher the quality score, the more likely you are to feature above your competition and solicit the click from the user.
Quality score applies to search ads, mainly expanded text ads which will be phased out by Google in 2022. It’s unclear whether this will stay or not but there is another metric called “Ad Strength” which is scored on similar factors.
Bidding
We touched on bidding methods earlier in the article, so now let’s visit bidding strategies.
It’s important to know the difference between both bidding methods & bidding strategies. Bidding methods are ways you, as the advertiser, are willing to pay for clicks/impressions on your ads. Bidding strategies are the way in which Google uses machine learning and other factors to deliver these ads to users.
There are a total of 11 different bidding strategies offered by Google Ads. We’ve taken the top 5 most commonly used bidding strategies and have aligned these with different business objectives.
The key bidding strategies are covered below:
- Target Impressions Share: Best suited to the business objective of raising visibility.
- Maximise Clicks: Best suited to the business objective of brand awareness.
- Maximise Conversions: Best suited to the business objective of leads/conversions.
- Target CPA: Best suited to the business objective of leads/conversions, where you know how much you want to spend to acquire a lead.
- Target ROAS: Best suited to the business objective of generating revenue.
Whatever your business objective, Google Ads can help your business to get in front of many potential customers.
Ads
Next, we’ll look at ads. What are they? What’s important to consider when creating ads?
Google Ads offer ads in various different formats, which are suitable for different placements all across the internet – we’ll cover this in more detail a little later on.
Ads are the way you display your message to users and potential customers. These can be text-based (search) or visual (display or video). Depending on what your objectives are and what you are trying to promote, depends on which types of ads you’ll want to use. e.g. You may run a shoe shop and would like to create ads for your products to increase sales, in this instance you’d probably want to look at Shopping & Display Ads.
It’s also worth noting that visual ads are typically better for, but not limited to, awareness based goals. You can also use these ads for conversion based objectives too.
So, what’s important to consider when creating ads in Google Ads?
Text: Headline, description, URLEnsure you create copy that includes the keywords you’re targeting. Also look to include USPs too (free shipping, etc.) as these may be the deciding factor to a user browsing many different brands promoting the same product or service as you.Visual: Logo, Product (written & Image), CTATell users who the brand is as soon as they view the ad. Make it obvious what you are promoting with the product/service name & image. Include a CTA to instruct the user of the next step they should take, “Get A Quote Now”.Video: Tell a story, invoke emotion in the userUsers are reacting better with ads that don’t seem like they are ads. Tell a story and make promotion of your product or service appear natural. Perhaps consider invoking a certain emotion in a user to make them feel instantly connected with the product/service/brand.
Other
At this point, you may be thinking “What else is there to know about Google Ads?”, and well in truth, a lot! But for now, let’s just cover the basics.
- Location: You can target or exclude users in specific geographic areas, you can apply bid adjustments too, meaning if your focus location is Birmingham, you might want to apply a 50% increase in your bids for this location.
- Audiences: You can target audiences that are created and collated by Google themselves. These audiences are created using machine learning to analyse different signals and turn these signals into insights. Those insights could be anything from a user’s purchase intent, user locations, average session duration, past search history, etc. These can be beneficial to help narrow down who you’re displaying your ads to.
- Schedules: You can choose when you want to display your ads. If you are closed on weekends, you may decide you don’t want to show ads on Saturday or Sunday you can turn them off. Another benefit of scheduling is that if you break up each day into segments, over time you’re able to see which days and times are most effective in terms of clicks and conversions. You’re also able to apply bid adjustments for the most/least effective days and times.
- Extensions: Extensions are ways of adding additional information to your ads. You can add USPs, links to other important pages, phone numbers and in some cases, images as extensions.
These are some examples of other attributes to consider when creating ads for your business using Google Ads, there are of course many other things that come into play but for now this is a good introduction.
Types Of Google Ads
Now you have an understanding of what Google Ads is and how it works, let's get into the different types of ads and their purposes.
Google Ads offers 8 different types of ads, each served best for different purposes and business objectives.
In this article, we’ll cover the main 5; Search, Display, Shopping, Video & App, but be aware of the other 3 ad types; Smart (automated ads), Local (drive users to a physical location) & Discovery (run ads when the store is open).
Search:
Search campaigns allow you to place ads across Google's vast network of search results. You can show ads to people actively searching online for your products and services. These ads are text-based and require you to create a list of keywords or search terms to target.
Display:
Display campaigns serve visually engaging ads on the Google Display Network. The Display Network helps you reach people as they browse millions of websites, apps and Google-owned properties (such as YouTube and Gmail).

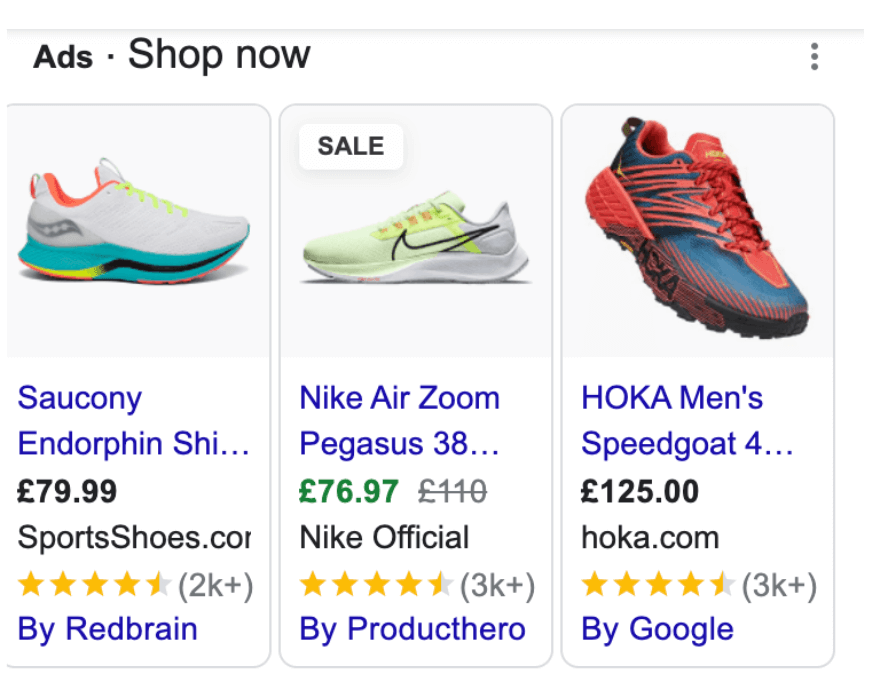
Shopping:
Shopping ads are ads that include rich product information, such as a product image, price and merchant name. These are a great way to showcase and promote individual products.
Video:
Video campaigns let you show ads in videos on YouTube and on websites and apps running on Google video partners. Video is a great way to get in front of users who may never have heard of your brand before.
App:
App campaigns streamline the process for you, making it easy to promote your apps across Google’s largest properties including Search, Google Play, YouTube, Discover on Google Search and the Google Display Network.

What else is there to know?
We’ve now covered the main basis for the platform, what it is, how it works and the different types of ads. I can hear you asking “well, what else is there to know?”, so let’s get into it.
Google Ads has built in tools for forecasting performance.
- Keyword Planner:
- The Keyword Planner is a great tool for forecasting spends, clicks, impressions & results for a certain set of keywords. You can also discover new or similar keywords that you may not have otherwise thought about. This tool provides insight about the potential performance of a suggested campaign before creating and running the campaign.
- Performance Planner:
- The Performance Planner is a handy tool for forecasting the performance of existing campaigns using historical data, machine learning and other factors. You can also review how the campaigns would perform if the budgets were increased/decreased. This can help you plan activity for the coming month and allow you good insight into the expected results for that period.
- Reach Planner:
- The Reach Planner is a planning tool that is designed to accurately plan for reach-based video campaigns across YouTube & other video partners’ websites and apps. Reach Planner shows reach and frequency estimates, but doesn’t guarantee performance. Actual campaign performance depends on other factors such as ad quality, ad relevance and campaign settings.
There are of course many things I haven’t managed to cover in this article but this certainly gives you a good starting point in terms of the things you need to know.
It’s also worth noting the proper account and campaign structure. The approach you should take when setting up a campaign is: Campaign > Ad group > Ads > Keywords. This hierarchy allows you to create multiple ad groups within a campaign and multiple ads in each ad group. e.g. if you run a shoe shop, you may want to create 2 campaigns (mens & womens), then different ad groups for trainers, hiking boots, smart shoes, etc.
Setting campaigns up with the recommended hierarchy also allows you to identify when things are working so you can hone in on what it is that’s working to improve your ROI.
How Do I Get Started?
Interested to know more? Here’s the next steps.
Firstly, you need to define what it is you’re looking to achieve from running Google Ads. What’s your business objective? For example, it could be you’re looking to raise awareness of your brand, or you could be looking to increase leads into the business.
You’ll then need to create a Google Ads account.
Once your objective is defined and your ad account has been created, you’ll need to choose the type of ads that you’re looking to run. As previously mentioned, different ads are suitable for different business objectives so you may need some expert help with this.
Next, you’ll need to define your target audience. This may seem an easy feat, however, you’ll need to be as detailed as possible to avoid targeting the wrong audience.

Now you’ve defined your target audience, the next step is to create the different ads you’re looking to run. If you decide to create display or video ads, you’ll need a designer or a videographer to help you with these.
The final step is to set up billing for the account. Earlier, we talked about setting monthly budgets to ensure you do not spend more than you allocate, this can be set up during billing too.
Congratulations, you’ve set up your own Google Ads account!
We’ve outlined an overview of Google Ads, the platform, what it is, how it works and the different features and the steps you should take if you’re looking to create your own account and run your own Google Ads.
However, if you’d like some expert help in this process or would rather pay someone to do this for you, Selesti are here to help. Contact us today with your requirements.


